Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
In FTIR spectroscopy, a sample (solid, liquid or gas) is irradiated with a multi-frequency infrared light beam and the amount of light absorbed is measured. The information obtained (the absorption at each wavelength) is unique depending on the chemical composition of the sample, which enables identification of, for example, a previously unknown substance. Typical uses are to identify:
- organic substances such as polymers, oils and fats
- inorganic substances such as minerals

Result (Example)
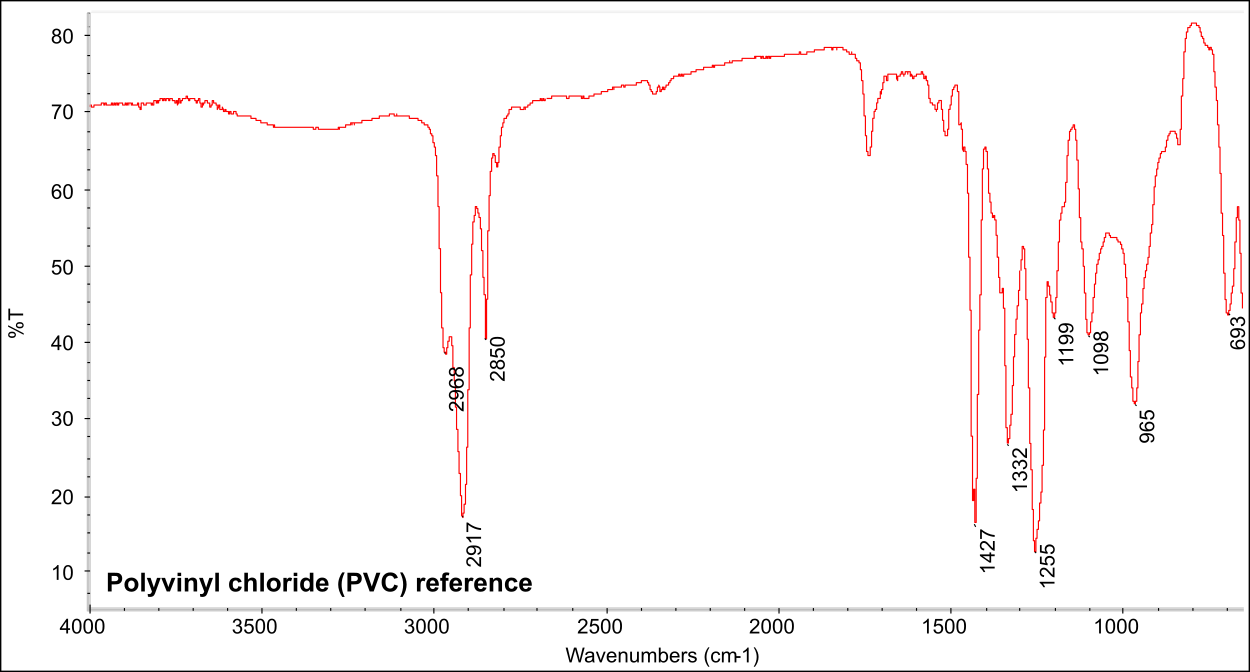
FTIR-spectrum for polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
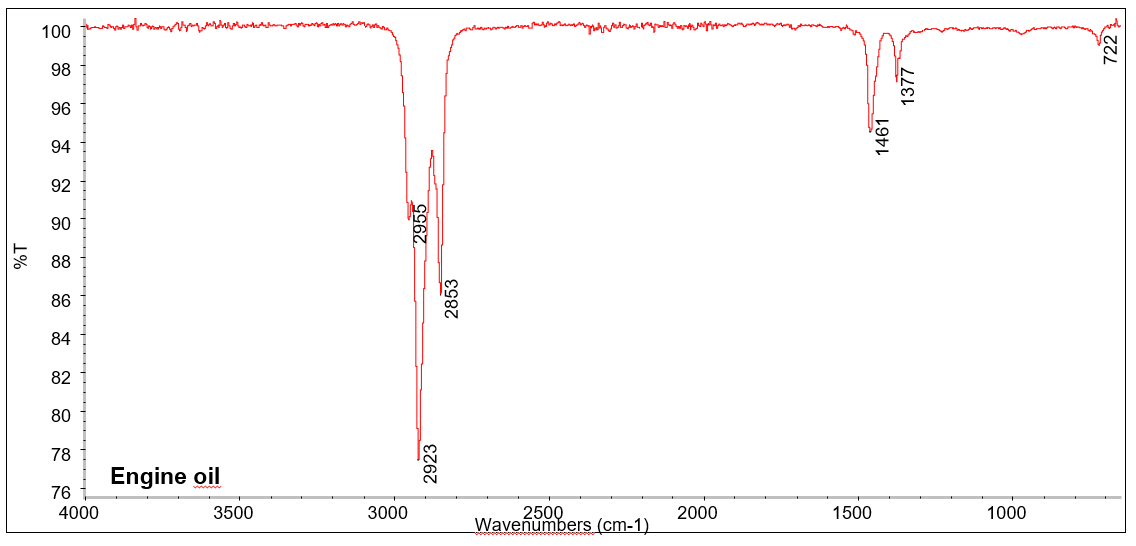
FTIR-spectrum for engine oil.

