X-ray fluorescence (XRF)
X-ray fluorescensce is a technique for chemical analysis (elemental analysis) of samples. In this technique (as in EDX), an energetic electron beam is focused on the sample. The incoming electron beam can excite electrons from the inner shells of the sample atoms. When this happens, the void in the inner shell of the atom is filled with an electron from an outer shell. At this transfer, X-ray photons are simultaneously emitted. The energy content of these X-ray photons is specific depending on which element they are emitted from and by analyzing the photons, the chemical composition in the sample is obtained.
XRF analysis equipment is available as stationary lab equipment but also a handheld equipment.
Applications are:
- detection of hazardous substances in products e.g. in plastics, paint, electronics
- RoHS
- REACH
- SVHC
- detection of heavy metals in soil samples
- non-destructive material analysis
- positive material identification (PMI) e.g. sorting of metals
- geochemical analysis in exploration industries
- analysis of noble metals

Result (Example)
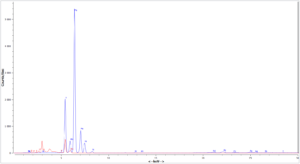
XRF-spectrum for stainless steel (EN 1.4404).

